[ad_1]
CBSE Class 12 Geography Syllabus 2022-2023 is presented here in PDF format. This revised syllabus mentions the course structure, course content and map work for CBSE Class 12 Geography subject.
CBSE Class 12 Geography Syllabus 2022-2023 is important to start early preparations for the CBSE Board Exam 2023 as it has all the essential elements that are important from the examination point of view. Students will get to know the course structure wherein they will have an idea of the weightage of different units of Geography for the board exam. This will help them to focus on the important units. The detailed syllabus will help them to prepare the appropriate content for the board exam in a planned manner so that they do not have to rush at the last moment. The details of the map work are also mentioned at the end of the syllabus along with the question paper design. Therefore, students should check the CBSE Class 12 Geography Syllabus 2022-23 thoroughly to prepare well for their board exams. Check and download the syllabus below.
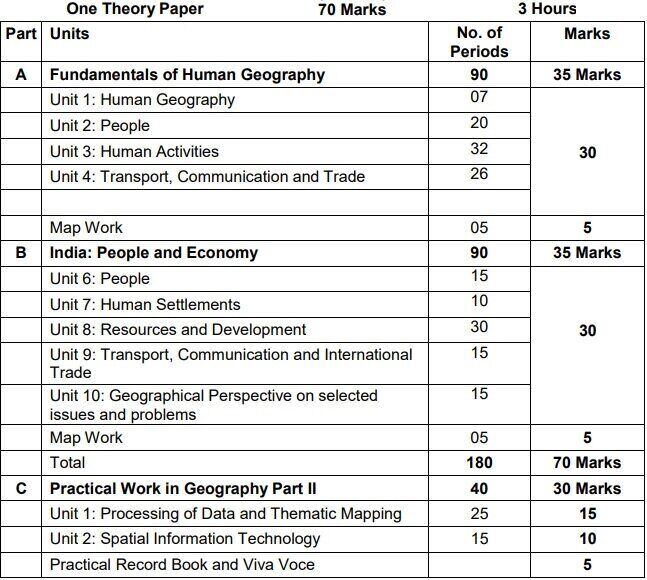
CBSE Class 12 Geography (Code No. 029) Course Structure 2022-23
Also Check CBSE Class 12 Syllabus of All Subjects for 2022-2023 Session (PDF)
CBSE Class 12 Geography Course Content 2022-2023
Part A: Fundamentals of Human Geography – 90 Periods
Unit 1: Human Geography: Nature and Scope 07 Periods
Unit 2: People – 20 Periods
The World Population- distribution, density and growth
Population change – Components of population change, Demographic Transition
Human development – concept; selected indicators, international comparisons
Unit 3: Human Activities – 32 Periods
- Primary activities – concept and changing trends; gathering, pastoral, mining, subsistence agriculture, modern agriculture; people engaged in agricultural and allied activities – some examples from selected countries
- Secondary activities- concept; manufacturing: types – household, small scale, large scale; agro based and mineral based industries;
- Tertiary activities – concept; trade, transport and tourism; services; people engaged in tertiary activities
- Quaternary activities- concept; people engaged in quaternary activities – case study from selected countries
Unit 4: Transport, Communication and Trade – 26 Periods
- Land transport – roads, railways; transcontinental railways Water transport- inland waterways; major ocean routes
- Air transport- Intercontinental air routes Oil and gas pipelines
- Satellite communication and cyber space
- importance and usage for geographical information; use of GPS
- International trade- bases and changing patterns; ports as gateways of international trade; role of WTO in international trade
Map Work on identification of features based on 1-5 units on the outline Physical/Political map of World. – 05 Periods
Part B: India: People and Economy 90 Periods
Unit 6: People – 15 Periods
- Population: distribution, density and growth; composition of population – linguistic, religious; sex, rural-urban and occupational-regional variations in growth of population
Unit 7: Human Settlements – 10 Periods
- Rural settlements – types and distribution
- Urban settlements – types, distribution and functional classification
Unit 8: Resources and Development – 30 Periods
- Land resources- general land use; agricultural land use; geographical conditions and distribution of major crops (Wheat, Rice, Tea, Coffee, Cotton, Jute, Sugarcane and Rubber); agricultural development and problems
- Water resources-availability and utilization irrigation, domestic, industrial and other uses; scarcity of water and conservation methods-rain water harvesting and watershed management
- Mineral and energy resources- distribution of metallic (Iron ore, Copper, Bauxite, Manganese); non-metallic (Mica, Salt) minerals; conventional (Coal, Petroleum, Natural gas and Hydroelectricity) and non-conventional energy sources (solar, wind, biogas) and conservation
- Planning in India- target group area planning (case study); idea of sustainable development (case study)
Unit 9: Transport, Communication and International Trade
- Transport and communication-roads, railways, waterways and airways: oil and gas pipelines; Geographical information and communication net works
- International trade- changing pattern of India’s foreign trade; sea ports and their hinterland and airports
Unit 10: Geographical Perspective on selected issues and problems – 15 Periods
- Environmental pollution; urban-waste disposal
- Urbanization, rural-urban migration; problems of slums
- Land degradation
Map work on locating and labeling of features based on aboveunits on outline map of India. (05 Periods)
Part C: Practical Work in Geography Part II – 40 Periods
Unit 1: Processing of Data and Thematic Mapping – 25 Periods
- Type and Sources of data: Primary, Secondary and other sources
- Tabulating and processing of data; calculation of averages, measures of central tendency
- Representation of data- construction of diagrams: bars, circles and flowchart; thematic maps; construction of dot; choropleth and isopleths maps
Unit 2: Spatial Information Technology – 15 Periods
- Introduction to GIS; hardware requirements and software modules; data formats; raster and vector data, data input, editing and topology building; data analysis; overlay and buffer.
Prescribed Books:
- Fundamentals of Human Geography, Class XII, Published by NCERT
- India – People and Economy, Class XII, Published by NCERT
- Practical Work in Geography Part II, Class XII, Published by NCERT
Download the full syllabus from the following link and check the details of map work as well:
[ad_2]
Source link







