[ad_1]
GS Paper 2
Syllabus: Government policies and Intervention
Source: Live Mint
Context: After liberalizing the use of geospatial data under the draft geospatial data policy in February 2021, the Ministry of Science and Technology has notified the National Geospatial Policy, 2022.
About the policy:
“The National Geospatial Policy, 2022 is a citizen-centric policy that seeks to strengthen the geospatial sector to support national development, economic prosperity and a thriving information economy
- Aim: The 13-year guideline promote the country’s geospatial data industry and develops a national framework to use such data for improving citizen services, and more.
- Themes: The policy has divided 14 Geospatial Data Themes to support the development of commercial geospatial applications in various sectors e.g., disaster management, mining, forestry etc.
- Technology Infrastructure:
- Geospatial Knowledge Infrastructure (GKI):
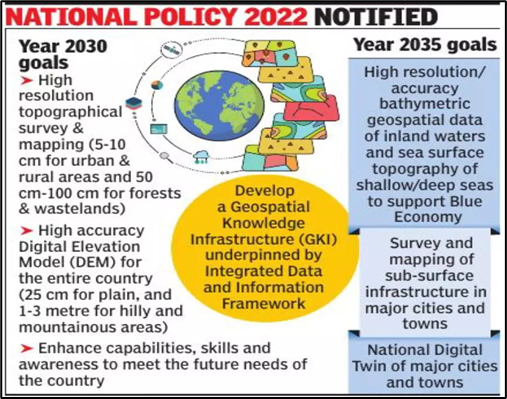
- The government will establish an Integrated Data and Information Framework by 2030 (to develop GKI)
- The government will also establish National Digital Twin (for high-resolution topographical survey and mapping by 2035)
- Institutional Infrastructure:
- Geospatial Data Promotion and Development Committee(‘GDPDC’) will be constituted for formulating and implementing guidelines, strategies, and programs for the promotion of activities related to the Geospatial sector.
- Will put in place a legal framework (by 2025) that supports the liberalization of the geospatial sector, and democratization of data for enhanced commercialization with value-added services.
- Geospatial Knowledge Infrastructure (GKI):

Significance of the policy:
- Increased Coverage: Government has opened its geospatial data and services offered by government agencies, academic and research institutions, private organizations, NGOs, and individuals.
- No prior approval required: Government has removed the requirement for prior approval, security clearance, or other restrictions on the management of geospatial data
- Self-Certification will be sufficient for adherence to the guidance
- Freehand at Processing of geospatial data: Anyone can process the acquired geospatial data, build new applications and solutions using it and use it for profit (except for defence or security-related data)
- Multi-dimensional Applications: E.g., economy, sustainable national development initiatives, Agriculture etc.
- Focus on ‘local’ relevance: The Policy recognizes the importance of locally available and locally relevant Maps and Geospatial Data
- Promoting Start-ups:The Policy enables and supports innovation, creation and incubation of ideas and start-up initiatives in the Geospatial sector
- Support India’s ‘Blue Economy’: By 2035, the policy will include mapping of sub-surface infrastructure in major cities and towns across India, and the development of accurate bathymetric geospatial data (resources and economy of inland waters, and sea surface topography of shallow and deep seas)
Applications of Geospatial data (in the Agriculture and Allied sector):
- Drive private participation and competitiveness in Agritech
- Wider Adoption of Precision farming: Precision farming combines the power of artificial intelligence (AI), Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS), and Big Data.
- Wider Adoption of Locational data: While the global positioning system (GPS) locates precise crop locations, the global information system (GIS) stores this data.
- This data later helps in Crop scouting, Soil sampling, Weed location, accurate planting, and harvesting.
- Better crop forecasting: The previous restriction on geospatial data had limited use of remote sensing data maps such as NDVI (Normalized Difference Vegetation Index).
- 4 Rs approach to reduce nutrient losses from farming systems (the Right Product, at the rightrate, at the right time, and at the right place)
- Better implementation of Government schemes such as PM Fasal Bima Yojana and ‘Per Drop more Crop’: Geospatial data will assist the BFSI (Banking, Financial Services, and Insurance) segment to understand the risk better and underwrite loans and insurance products.
- Increased Landholding size: Along with the SWAMITVA scheme, the geospatial data will help in the pooling of lands by farmers. This will drive wider adoption of Commercial and Precision Farming in India
- Allow development of ecosystem markets:
- g., the GIS nitrogen trading tool is used to assess the effects of the implementation of conservation practices on reductions in nitrate leaching and GHG emissions that could be traded in air and water quality markets
Allied sectors
- Fisheries: better geospatial data will drive more targeted and deeper fishing opportunities, thus helping in the economic upliftment of fishermen
- It will help bridge the infrastructure gap as envisaged under PM Matsay Sampada Yojana
- Dairy: Geospatial data can help in better grazing grounds for cattle and their management
- Minor Forest Produce: Tribal collection of MFP and marketing of their products can be advanced using geolocation data in deep forests
- g., MoEF & CC is using LiDAR technology to map out water requirements within the forest
- Ridge-to-valley approach: It seeks to detain, divert, store and use available rainwater using geospatial data








Other Government initiatives in this direction:
SWAMITVA Scheme (Survey of Villages and Mapping); Drone sector (The Drones Rules 2021); India opened its space sector to private entities and 5G technology; PM Gati Shakti Masterplan (Infrastructure development is powered by geospatial technology); Digital Ocean platform (for the management of our oceans)
Insta Links
Geospatial data policy liberalized
Mains Link
Q. Democratizing geospatial data will enable the rise of new technologies & platforms that will drive efficiencies in agriculture and allied sectors. Discuss (15M)
Q. What is Geo-Spatial data? Comment upon the present Policy on Geospatial Data in the country while emphasizing the liberalization aspect (10M)
Prelims Link:
- What is geospatial data?
- Applications.
- Policy on geospatial data.
- Recent changes.
[ad_2]
Source link