[ad_1]
75 Years of Independence Celebration: Modern India is an epitome of Scientific and Technological Development and is one of the key elements for economic growth. Post 15th August 1947, India’s journey has become a great example of an impressive growth story. As claimed by the Indian Brand Equity Foundation, India is among the topmost countries in the world in the field of scientific research and has been positioned as one of the top five nations in the field of space exploration. India has continuously undertaken space missions, including missions to the moon and the famed Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV). India also ranks third among the most attractive investment destinations for technology transactions in the world.
Know 75 Years of India’s Independence Journey including Major Achievements
75 Years of India’s Independence: Major Scientific & Technological Developments
Our First Prime Minister, Pandit Jawahar Lal Nehru said “Science is not merely an individual’s search for truth; it is something infinitely more than that if it works for the community”. He made efforts to convert India’s economy into that of a modern state and to fit her into the nuclear age and do it quickly. As India is celebrating the 75th anniversary of its independence, let’s look what were the major Scientific & Technological developments during this period:
Know Your National Flag: Interesting and Amazing facts about India’s Tiranga
Development of Agricultural Technology
As per the official data, the agriculture sector forms only about 18% of India’s GDP and employs almost 65% of the total workforce. Technology plays an important role in the agriculture and sustainable development of India. Advanced technology helps in developing and improving many areas of agriculture, such as fertilizers, pesticides, seed technology, etc. Let’s look at some of the major milestones of Agriculture Technological Development in India Post-Independence:

The Green Revolution was an endeavor initiated by Norman Borlaug in the 1960s. He is known as the ‘Father of Green Revolution in the world. It led to him winning the Nobel Peace Prize in 1970 for his work in developing High Yielding Varieties (HYVs) of wheat.

Operation Flood, launched on 13 January 1970, was the world’s largest dairy development program and a landmark project of India’s National Dairy Development Board.
Development of Defence Technology
Dr. Homi Bhabha has played a major Role in the Development of Defence Technology in India after Independence. India has been attacked many times by its neighbors. India has faced many wars including Indo China War and Indo-Pakistan War and has also won many battles. Let’s look at some of the major milestones of Defence Technological Development in India Post-Independence:

The Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) was set up in 1958 to secure the borders of India with more advanced Defence Technology. Since then, DRDO has developed several large programs and essential technology, including aircraft, small and large arms, artillery systems, electronic warfare (EW) systems, tanks, and armored vehicles, sonar systems, command and control systems, and missile systems.
|
1989: Agni Missile was successfully launched |

Agni-I was first tested at the Interim Test Range in Chandipur at 7:17 AM on 22 May 1989 and was capable of carrying a conventional payload of 1,000 kg (2,200 lb) or a nuclear warhead. Agni missiles consist of one (short range) or two stages (intermediate-range).
|
1998: India conducted Pokhran-II tests |

On 11 and 13 May 1998, twenty-four years after Pokhran-I, the Indian Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) and Atomic Energy Commission (AEC) conducted five further nuclear tests, dubbed “Pokhran-II”, at the Pokhran range. The chief scientific adviser and the Director of Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO), Dr. Abdul Kalam, and Dr. R. Chidambaram, the Director of the Department of Atomic Energy (DAE), were the chief coordinators of this test planning.
Development of Space Technology
India has initiated some major space research programs under the vision of some great scientists and leaders like C.V Raman, Dr. Vikram Sarabhai, Dr. A.P.J Abdul Kalam, etc. Let’s look at some of the major milestones of Space Technological Development in India Post-Independence:
|
1963: India’s first-ever rocket launch |

The launch of the first sounding rocket from Thumba near Thiruvananthapuram, Kerala on 21 November 1963, marked the beginning of the Indian Space Programme. Sounding rockets made it possible to probe the atmosphere in situ using rocket-borne instrumentation. This was the first milestone in modern India’s space odyssey. Dr. Vikram Sarabhai and his then accomplice Dr. APJ Abdul Kalam were the brainchild of this achievement.
|
1975: First Satellite Aryabhata launched |
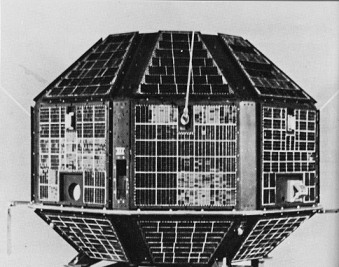
Aryabhatta, the first Indian satellite, was launched by the Soviet Union in 1975. The Aryabhata spacecraft, named after the famous Indian astronomer, was India’s first satellite; it was completely designed and fabricated in India and launched by a Soviet Kosmos-3M rocket from Kapustin Yar on April 19, 1975.
|
1969: Formation of Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) |

ISRO was formed in 1969 with a vision to develop and harness space technology in national development while pursuing planetary exploration and space science research. ISRO replaced its predecessor, INCOSPAR (Indian National Committee for Space Research), established in 1962 by India’s first Prime Minister Pt. Jawaharlal Nehru and scientist Vikram Sarabhai, are considered among the founding fathers of the Indian space program.
|
2008: Chandrayaan-1 launch |

Chandrayaan-1 was the first Indian lunar probe under the Chandrayaan program which was launched by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) on October 22, 2008. The mission was a major boost to India’s space program, as our country researched and developed its own technology to explore the Moon.
|
2013: Mangalyaan launched |

The Mars Orbiter Mission (MOM), also called Mangalyaan, is a space probe orbiting Mars since 24 September 2014. It was launched on 5 November 2013 by the Indian Space Research Organisation.
Who is the Original Designer of India’s National Flag?
The journey highlights India’s expansion ranging from agricultural production to nuclear and space technology, from affordable health care to world-class educational institutions, from Ayurveda to biotechnology, from giant steel plants to becoming an IT power, and having the third-largest start-up ecosystem in the world.
[ad_2]
Source link








